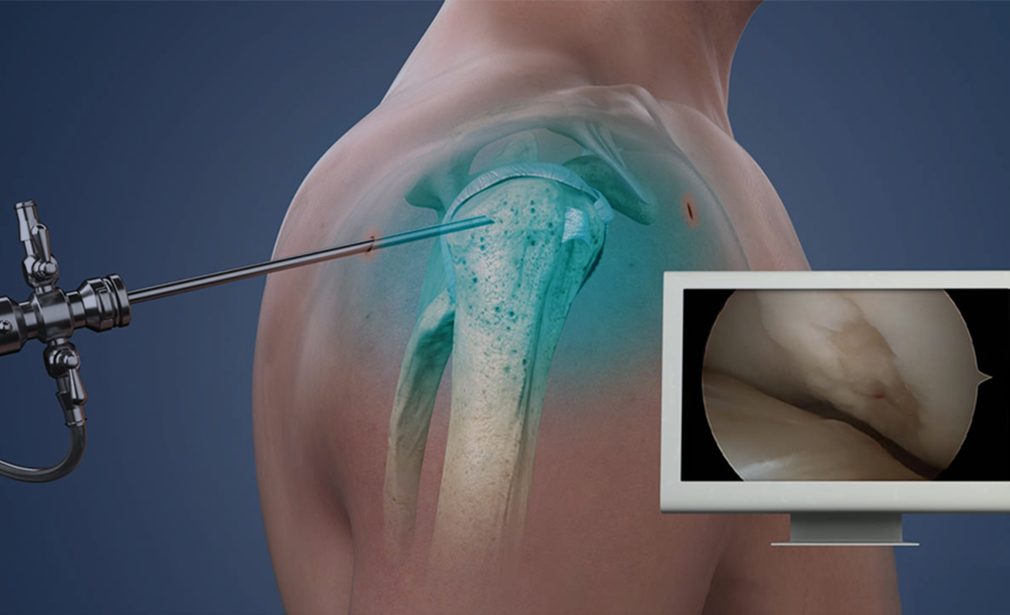
Shoulder Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows orthopedic surgeons to diagnose and treat various shoulder conditions using a small camera called an arthroscope. This technique involves making small incisions, through which the arthroscope and specialized instruments are inserted into the shoulder joint. The camera transmits images to a monitor, enabling the surgeon to perform precise procedures with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues.
This method is use to treat tear in the shoulder muscle (Rotator Cuff) as well as injuries to the socket of the shoulder (labrum injury) through this surgery. We reduce the torn soft tissues back to their natural location, through key-holes, allowing us to regain and restore our normal shoulder fucntion,Thus treating recurrent shoulder dislocation and regaining normal rotational function of the shoulders.
The advantages of shoulder arthroscopy over traditional open surgery include: 1) Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions lead to less tissue damage. 2) Reduced Pain: Typically results in less postoperative pain. 3) Quicker Recovery: Shorter hospital stays and faster return to normal activities. 4) Lower Risk of Infection: Smaller incisions reduce the risk of infection. The most common symptoms of shoulder arthroscopy are:
- Mild to moderate pain is common post-surgery. This discomfort may be more noticeable at night and can disrupt sleep
- It's normal to have swelling in the shoulder area, as well as in the hand and arm on the operated side. This typically resolves within a few days.
- You might notice skin discoloration near the incision sites. This is a normal part of the healing process.
- Some stiffness in the shoulder joint is expected. Engaging in prescribed physical therapy exercises can help improve mobility
- Temporary numbness or tingling in the fingers or hand may occur due to positioning during surgery. This usually resolves within a few weeks.
- A feeling of weakness in the shoulder is common. This should improve as you progress through your rehabilitation program.
- You may experience difficulty moving your arm in certain directions. This limitation often improves with physical therapy.
- Feeling tired for several days after surgery is normal. Ensure you get adequate rest to support the healing process.
Frequently asked questions
Shoulder arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat various shoulder conditions. If you’re considering this surgery, you may have several questions. Here are some common FAQs:
Shoulder arthroscopy involves inserting a small camera (arthroscope) through tiny incisions in the shoulder to visualize and treat joint issues. This technique allows for precise repairs with minimal tissue disruption.
This procedure can address various shoulder problems, including:
Rotator cuff tears
Labral tears
Shoulder impingement syndrome
Biceps tendon injuries
Frozen shoulder
Shoulder instability
The duration depends on the specific procedure performed. For example, arthroscopic rotator cuff surgery typically takes 1-2 hours.
Recovery varies based on the procedure:
Initial Rest: A period of rest to allow healing, with the use of a sling to support the shoulder.
Physical Therapy: A structured rehabilitation program to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
Gradual Return to Activities: A phased approach to resuming daily activities and sports, based on the surgeon’s recommendations.
The timeline for returning to work or daily activities depends on the nature of your job and the specific procedure performed. It’s important to follow your surgeon’s advice to ensure proper healing.
Advantages include:
Smaller incisions
Reduced pain
Quicker recovery time
Lower risk of infection
These benefits contribute to a more comfortable and efficient recovery process.